Cualquiera que haya utilizado un audífono sabe que, aunque el dispositivo funciona bien en entornos silenciosos, puede tener dificultades para distinguir el habla del ruido circundante en un entorno ajetreado o ruidoso. La reducción del ruido es un indicador importante de la calidad de un audífono.
Muchos usuarios han notado que la claridad del habla en el probador es mucho mejor que en un entorno ruidoso en la calle. Esta diferencia se debe a que el ruido ambiental interfiere en el habla, dificultando una audición clara aunque se pueda oír el sonido. Para solucionar este problema, debemos hablar de las tecnologías de reducción del ruido de los audífonos, que son uno de los factores clave que explican las diferencias de precio entre unos dispositivos y otros.
Antigua tecnología de reducción del ruido de los audífonos
Los audífonos antiguos, debido a las limitaciones de la tecnología de chip, no eran capaces de distinguir completamente entre el habla y el ruido. Normalmente utilizaban una compresión multicanal básica. En términos sencillos, como el ruido suele originarse en las frecuencias bajas, estos dispositivos reducen automáticamente la amplificación de los sonidos de baja frecuencia en los modos ruidosos, "filtrando" esencialmente parte del ruido.
Este enfoque hace que la escucha sea más cómoda, pero también puede filtrar el habla que es similar al ruido de baja frecuencia. Como resultado, la claridad del habla no se maximiza del todo, lo que reduce la calidad general de la reproducción del sonido.
Nuevas tecnologías de reducción del ruido en audífonos
Con el desarrollo de la tecnología de chip inteligente, los audífonos modernos utilizan ahora técnicas de reducción del ruido más avanzadas y diversas, que combinan varias tecnologías, como la supresión del ruido (tecnología de chip) y la tecnología de micrófono.
1. Supresión del ruido
La supresión de ruido es la tecnología estándar de reducción de ruido utilizada en los audífonos modernos. A diferencia de los dispositivos más antiguos, los nuevos modelos analizan y diferencian el habla del ruido mediante el procesamiento digital de señales en los dominios del tiempo y la amplitud. A continuación, el procesador reduce la amplificación para el ruido y aumenta la amplificación para el habla, en lugar de comprimir indiscriminadamente todos los sonidos.
Sin embargo, a medida que han ido aumentando las exigencias de calidad de vida de los usuarios, la supresión básica del ruido ya no puede satisfacer las necesidades de todos. En entornos muy ruidosos y complejos, aunque el ruido se suavice, la mejora del habla puede seguir siendo insuficiente. Muchos usuarios siguen teniendo dificultades para comprender el habla en entornos auditivos difíciles.
2. Tecnologías de micrófono
La tecnología de los micrófonos desempeña un papel fundamental en la mejora del rendimiento de los audífonos en entornos ruidosos. Estos son algunos de los principales tipos de micrófonos utilizados en los audífonos modernos:
(1) Micrófonos direccionales fijos
En la vida cotidiana, el ruido puede venir de delante, de detrás o de los lados. Muchos audífonos están equipados con micrófonos direccionales o micrófonos que pueden identificar automáticamente la fuente de sonido principal. Estos micrófonos amplifican los sonidos de la parte frontal, que es por donde suele comunicarse el usuario, al tiempo que reducen los sonidos de los laterales y la parte posterior, suprimiendo eficazmente el ruido no deseado.
Con cierta experiencia, los usuarios pueden ajustar la posición de la cabeza en entornos ruidosos para minimizar el ruido de fondo. Por ejemplo, en un restaurante ruidoso, los usuarios pueden desplazar su silla para reducir el ruido de la cocina u otras fuentes.
(2) Micrófonos direccionales automáticos
La mayoría de los audífonos infantiles incorporan ahora micrófonos direccionales automáticos. Dado que los niños pueden carecer de la experiencia auditiva necesaria para realizar ajustes manuales, estos micrófonos seleccionan y amplifican automáticamente los sonidos de frente, al tiempo que reducen el ruido de fondo. La calidad de esta funcionalidad depende de la sofisticación de la tecnología utilizada.
(3) Direccionalidad adaptativa (multicanal)
Esta función, presente en muchos modelos de gama media y alta, ajusta la direccionalidad del micrófono en función del entorno. Los micrófonos direccionales adaptativos no sólo ajustan automáticamente el enfoque del micrófono, sino que también identifican la fuente de ruido y la suprimen. Algunos modelos avanzados pueden rastrear varias fuentes de ruido y reducirlas simultáneamente.
(4) Micrófonos omnidireccionales
En algunas situaciones concretas, los micrófonos direccionales pueden no ser la mejor opción. Por ejemplo, al conducir, si el audífono se centra en reducir el ruido de la parte trasera, puede limitar la capacidad de oír a los pasajeros de atrás. Los micrófonos omnidireccionales permiten a los usuarios oír los sonidos procedentes de todas las direcciones por igual, lo que proporciona una mejor experiencia en entornos como las salas de música, donde el sonido procede de múltiples direcciones. En estos entornos, el dispositivo puede cambiar automáticamente al modo omnidireccional para optimizar la experiencia auditiva.
(5) Audífonos personalizados con micrófonos direccionales
Algunos audífonos a medida, como los de conducto auditivo profundo, pueden tener un espacio limitado para funciones de micrófono más complejas. En estos casos, los usuarios dependen más de la estructura de su oído externo para ajustar la dirección y la calidad del sonido, lo que puede no ser tan eficaz para identificar y amplificar el habla.
¿Se puede eliminar completamente el ruido?
En la actualidad, ningún audífono puede eliminar completamente el ruido ni reproducir totalmente la experiencia auditiva de un oído normal. Sin embargo, es esencial recordar que incluso las personas con audición normal viven en entornos ruidosos y deben mantener conversaciones en medio del ruido ambiente. El ruido forma parte de nuestra vida cotidiana y, al igual que las personas con audición normal luchan contra el ruido, los usuarios de audífonos se enfrentan a retos similares. Unas expectativas realistas sobre la reducción del ruido son la clave de la satisfacción con cualquier audífono.
También hay que tener en cuenta que los audífonos con mejor tecnología de reducción del ruido suelen tener un precio más elevado. Por lo tanto, encontrar un dispositivo que se adapte a las necesidades del usuario proporcionará la mejor relación calidad-precio.
Componentes de micrófono ECMIC para audífonos
Micrófono de audífono (ECM-B4015AML39-733) para mejorar la claridad del sonido en entornos ruidosos
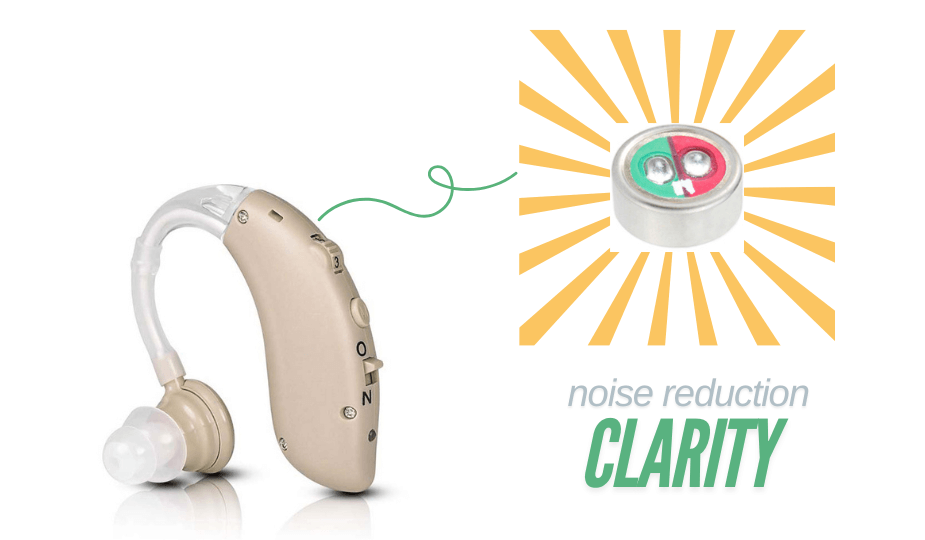

En ECMIC estamos especializados en producir micrófonos electret de alta calidadcomo el ECM-B4015AML39-733diseñado específicamente para aplicaciones de audífonos. Con características como alta sensibilidad (-39dB) y excelente relación señal/ruido (74 dB), nuestros micrófonos ofrecen una claridad de sonido superior y un mejor reconocimiento del habla, incluso en entornos ruidosos difíciles. Estos micrófonos están fabricados para ofrecer una calidad de sonido clara y uniforme, lo que contribuye a una mejor experiencia con los audífonos.
Para más información sobre nuestros componentes de micrófono y cómo pueden mejorar el diseño de su audífono, póngase en contacto con nosotros.