Miniature microphones are the most widely produced type of microphones globally, categorized primarily into electret microphones and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) microphones. These microphones are integral components found in everyday devices, ranging from mobile phones and computers to Bluetooth headsets. This article explores the operational principles and applications of these two types of miniature microphones.

Electret Microphones
Electret microphones, also known as electret condenser (ECM) microphones, use a dielectric material called an electret, which inherently carries a charge. This inherent charge forms a capacitor with the diaphragm, effectively providing its own bias voltage.

Electret microphones require a FET (Field-Effect Transistor) to convert impedance. They do not necessitate an external bias voltage, simplifying circuit design, typically needing only power for the FET. Many electret microphones integrate the FET directly within the microphone capsule, leaving only two connection terminals exposed. With advancements in manufacturing technology, electret microphones have become very small, with some having a diameter as small as 3mm. Furthermore, to withstand high-temperature reflow soldering for PCB assembly, Surface-Mount Device (SMD) versions of electret microphones have been developed.

Advantages and Applications:
- Simple Structure: No need for an external bias voltage, leading to simpler circuit designs.
- Compact Size: Ideal for lavalier and headset microphones.
- Wide Application: Extensively used in recording studios, live music performances, and concert hall recordings.
- Advancements: Ongoing improvements in manufacturing technology have significantly enhanced the performance and quality of electret microphones.
MEMS Microphones
MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) microphones, also known as silicon microphones, are smaller and are widely employed in modern smartphones, computers, and various applications.

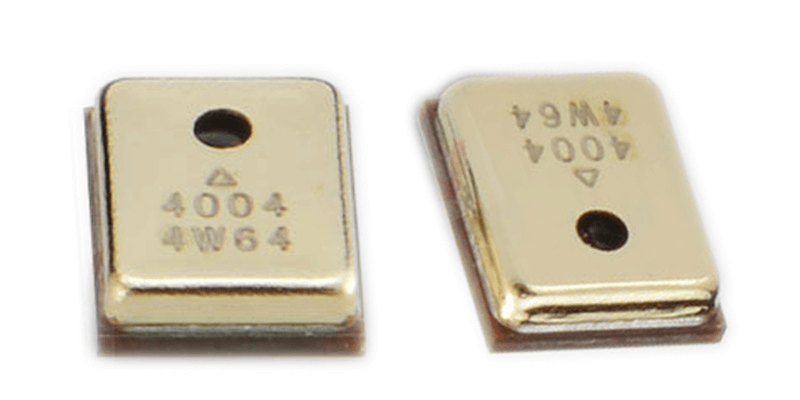
A typical MEMS microphone designed for audio capture comprises an ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) chip and a pressure sensor, both housed in a durable shell. Sound waves enter through an opening and interact with the diaphragm and base, forming a chamber. The ASIC chip is specifically designed and packaged to be an integral part of the MEMS microphone system, controlling the bias voltage on the pressure sensor and measuring capacitance changes to generate output signals.
Working Principle and Design:
- Integrated Design: Incorporates an ASIC chip and pressure sensor within a robust enclosure.
- Efficient Signal Processing: The ASIC chip manages bias voltage on the pressure sensor and processes signals by measuring capacitance changes. It integrates ADC and control I/O, directly outputting 1-bit PDM digital audio.
Conclusion
Continuous advancements in miniature microphone technology have expanded their applications across various devices. Electret microphones and MEMS microphones, representing the forefront of miniature microphone technology, play indispensable roles in diverse fields. As suppliers of microphone components, we are committed to delivering high-quality products that meet diverse application requirements.
Explore more articles on our website to delve deeper into miniature microphones and stay updated on the latest technology trends.


