In modern audio devices, microphone components (commonly known as “mic heads”) play a crucial role as core components of sound quality. Whether used in outdoor audio equipment, smart devices, or regular consumer electronics, the selection and application of microphone components directly impact product performance. This importance is particularly heightened in harsh environments, where the significance of waterproof microphone components becomes increasingly evident. This article will provide a detailed analysis of the differences between waterproof and regular microphones, as well as the waterproof design principles of omnidirectional and unidirectional microphones, helping to better understand the applicable scenarios for these microphone components.
Waterproof Microphone vs. Regular Microphone
1. Characteristics of Waterproof Microphones
- Waterproof Design: Waterproof microphone components are designed for outdoor, humid, or extreme environments. They can operate normally in conditions involving water, dust, and other harsh elements. The waterproof rating typically reaches IP67, meaning they can completely block dust and continue to work at a depth of 1 meter underwater for 30 minutes.
- Applications: Waterproof microphones are widely used in devices that need to withstand severe weather or moist environments, such as smartwatches, Bluetooth speakers, outdoor surveillance cameras, etc.
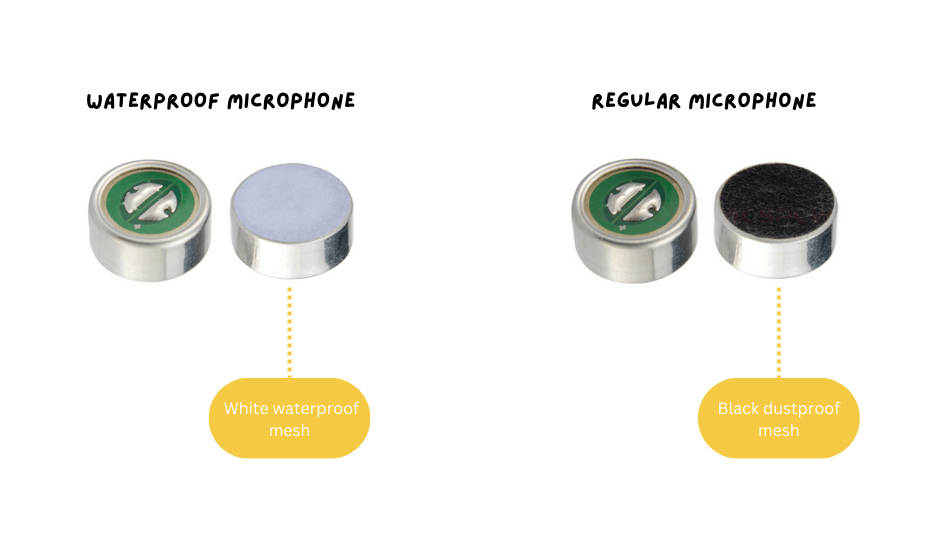
2. Characteristics of Regular Microphones
- On the other hand, regular microphones do not have specialized waterproof features. They are typically used in indoor environments or other scenarios where specific protection is not required. Regular microphone components usually come with a standard dustproof mesh, often in black, which can prevent some dust but cannot resist moisture.
- Dustproof Design: The dustproof mesh of regular microphones effectively prevents dust from entering the microphone, ensuring the cleanliness of internal components and the stability of long-term use.
- Applications: These microphones are widely used in everyday electronic devices such as smartphones, headphones, and laptops, suitable for use in dry environments.
Waterproof Principles of Omnidirectional and Unidirectional Microphones
1. Waterproof Principles of Omnidirectional Microphones
- Omnidirectional microphones pick up sound evenly from all directions, without the need to optimize for specific directions. Therefore, waterproof omnidirectional microphones typically achieve waterproofing through a sealed panel design. Specifically, the microphone’s panel is completely sealed without openings, effectively preventing water or dust from entering the interior and ensuring the device’s longevity in harsh conditions.
- Advantages of Waterproofing: The fully enclosed panel design greatly enhances the waterproof performance of omnidirectional microphones, making them particularly suitable for outdoor or moist environments.
- Applications: Waterproof omnidirectional microphones are widely used in smart homes, outdoor audio equipment, and other devices that need to be exposed to external environments for long periods.
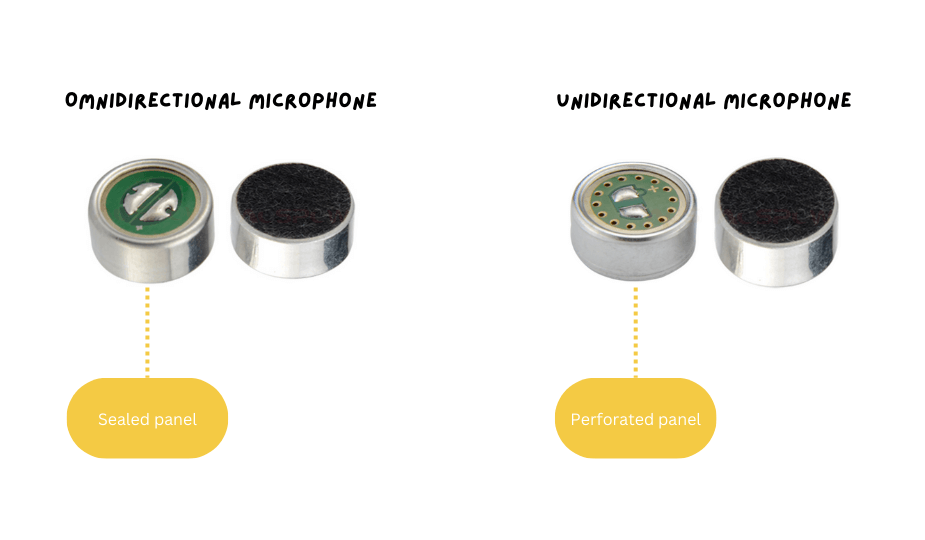

2. Waterproof Principles of Unidirectional Microphones
- Unidirectional microphones primarily pick up sound from a specific direction and are often used in applications requiring precise sound pickup, such as conference systems and video cameras. Therefore, the panel of unidirectional microphones usually has openings to enhance directional sound capture. However, this design prevents unidirectional microphones from achieving waterproofing through their own structure, as the openings make it easier for water to enter the microphone’s interior.
- Waterproof Challenges: Due to the necessity of openings on the panel, unidirectional microphones cannot achieve waterproofing on their own. They require additional waterproofing designs in the external structure of the product.
- Applications: These microphones are commonly used in directional audio devices, such as high-quality recording equipment, conference systems, and video cameras. To ensure waterproof performance, additional waterproof protection measures are typically added to the external design of the device, such as waterproof housings or additional protective covers..
Summary
Waterproof microphone components differ significantly from regular microphone components in design and application. Waterproof microphones achieve effective water and dust resistance through specialized waterproof meshes and sealed panel designs, making them ideal for outdoor or moist environments. In contrast, regular microphones focus on everyday dust protection, suitable for indoor or dry environments. Omnidirectional microphones, with their sealed panel design, can more easily achieve waterproofing, while unidirectional microphones rely on external product shell designs to provide waterproof protection.
Whether choosing waterproof or regular microphones, the decision should be based on specific usage scenarios. Waterproof microphones are particularly suitable for devices that need to withstand water or moist environments, while regular microphones are sufficient for everyday use. Additionally, for devices requiring directional sound pickup, although unidirectional microphones cannot provide waterproofing on their own due to their panel openings, incorporating external waterproofing structures can effectively enhance product durability.


