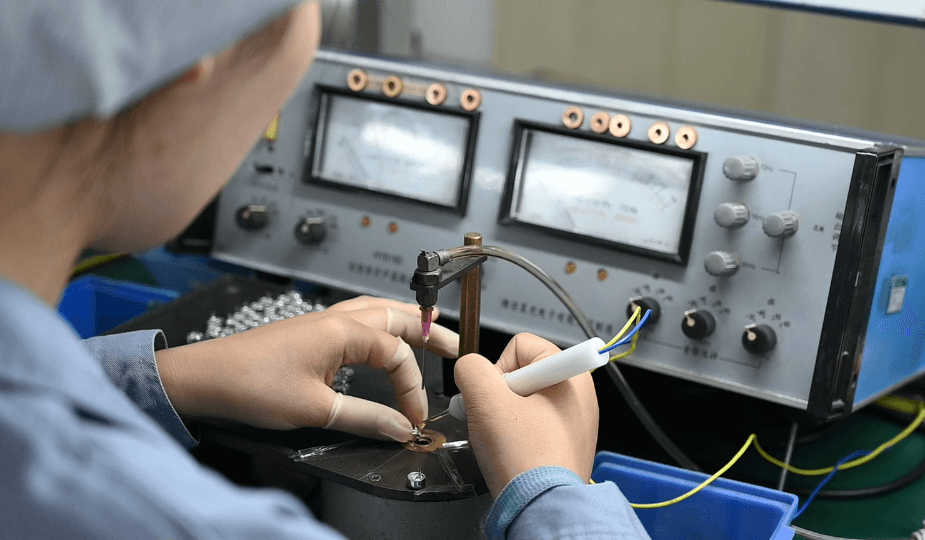
A technician carefully tests the sensitivity of an electret microphone capsule to ensure consistent audio quality.Electret condenser microphones (ECMs) are widely used in communication devices, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. Their performance depends heavily on two key parameters: sensitivity and current consumption. Understanding and accurately testing these parameters is essential to ensure stable performance across devices and applications.
1. What Do Sensitivity and Current Tell Us?
Sensitivity (dB)
Microphone sensitivity is expressed in negative dB values, such as -30dB or -40dB. A higher (closer to 0) value means the microphone is more sensitive to sound. For example, a -30dB mic will capture weaker or more distant sounds better than a -40dB one.
Working Current (μA)
Measured in microamperes (μA), the current indicates how much power the microphone draws during operation. More importantly, it indirectly reflects the internal FET amplifier’s gain. Stable current typically means stable FET performance.
2. Why Accurate Testing Is Crucial
- Device compatibility: Different host systems and audio circuits require specific mic parameters for optimal performance.
- Quality consistency: Batch testing ensures each unit meets design specifications. Deviations in current can signal gain issues inside the FET.
- Design reference: Developers rely on accurate data to select proper load resistors and supply voltage. Common values include 2.2KΩ and 2V.
3. How Sensitivity and Current Are Tested
Standard mic testing includes:
- Setting the working voltage: typically 1V, 2V, 2.5V, 3V, 4.5V, or 6V
- Setting the load resistor: options like 680Ω, 1KΩ, 1.5KΩ, 2KΩ, 2.2KΩ, and 3KΩ are available
- Connecting probes to mic terminals and reading the values
Example results:
- Sensitivity @ 1000Hz: -31.7dB
- Sensitivity @ 70Hz: -32.6dB
- Working current: 224μA
4. Our In-House Quality Inspection Practices
As a microphone component manufacturer, we follow strict quality control throughout the entire production cycle to ensure every unit performs reliably.
Multi-stage Inspection System
- IQC (Incoming Quality Control): Verifies components like FETs and solder joints before assembly.
- IPQC (In-Process Quality Control): Tests during key production stages to detect early deviations.
- OQC (Outgoing Quality Control): Final check before shipment ensures specs match customer requirements.
Automated Precision Assembly
Critical steps—such as amplifier soldering, diaphragm placement, and case sealing—are handled with automation to reduce human error and improve consistency. Sensitivity variation is controlled within ±1dB across the same batch.
Customer Benefits
- Reduced testing and calibration time on the client side
- Lower failure rates and returns due to parameter mismatch
- Better consistency in final audio performance
Conclusion
Though small in size, electret microphone elements require precise control over sensitivity and current for reliable use. Through detailed testing and quality control, we ensure each mic capsule delivers stable performance that meets our customers’ expectations.
Interested in exploring our range of high-quality microphone components? Browse our Electret Microphone Series here →


