Pour choisir le bon microphone avec une réponse en fréquence appropriée, il faut comprendre quelques aspects clés :
- Quelle source sonore allez-vous enregistrer ?
- À quoi ressemble l'environnement d'enregistrement ?
- Quelle est la méthode d'enregistrement ?.
Voyons quelques exemples :
1. Réponse en fréquence pour l'enregistrement de la voix off
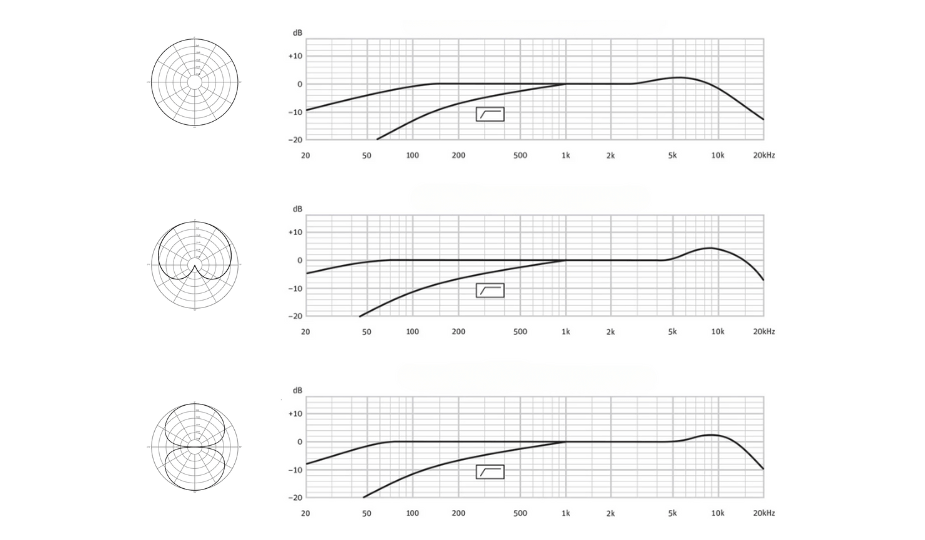
Les enregistrements de voix off sont généralement réalisés dans un studio contrôlé, avec un minimum de bruit et de réflexions sonores. Dans ces conditions idéales, un microphone avec une réponse en fréquence plate est le meilleur choix pour capturer des voix naturelles et précises.
Caractéristiques principales d'une réponse en fréquence appropriée pour les doublages :
- Modèles omnidirectionnels, cardioïdes ou en huit : En fonction de la configuration, ces directivités permettent de capter efficacement la voix tout en gérant l'acoustique de l'environnement.
- Atténuation des basses fréquences : une légère atténuation des basses fréquences permet d'éliminer les bruits tels que les grondements ou les vibrations.
- Accentuation des hautes fréquences (6 kHz à 12 kHz) : Une modeste accentuation de 2 à 3 dB dans cette plage ajoute de la luminosité et de la clarté à l'enregistrement, améliorant ainsi la présence vocale.
2. Réponse en fréquence pour les spectacles vocaux en direct
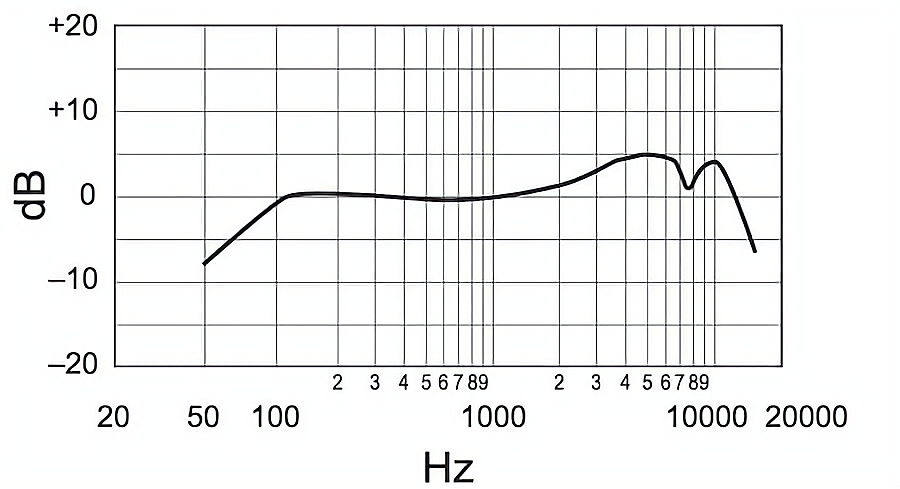
Les concerts se déroulent souvent sur des scènes bruyantes, avec d'autres instruments, le bruit de la foule et la réverbération de la salle. Dans ce cas, les microphones à directivité cardioïde sont préférables, car ils se concentrent sur le son situé directement devant le micro et rejettent les bruits indésirables. En outre, ces microphones sont souvent placés près du chanteur, ce qui peut provoquer un effet de proximité, renforçant les basses fréquences.
Caractéristiques principales de la réponse en fréquence appropriée pour les voix en direct :
- Low-End Roll-Off : Réduit les vibrations de la scène et le bruit de ronflement de l'alimentation.
- Réponse plate de 100 Hz à 2 kHz : Capture avec précision l'essentiel de la gamme vocale.
- Boost de 3 kHz à 10 kHz : Améliore la clarté de la voix, l'aidant à se détacher du mixage.
3. Réponse en fréquence pour l'enregistrement de la caisse claire
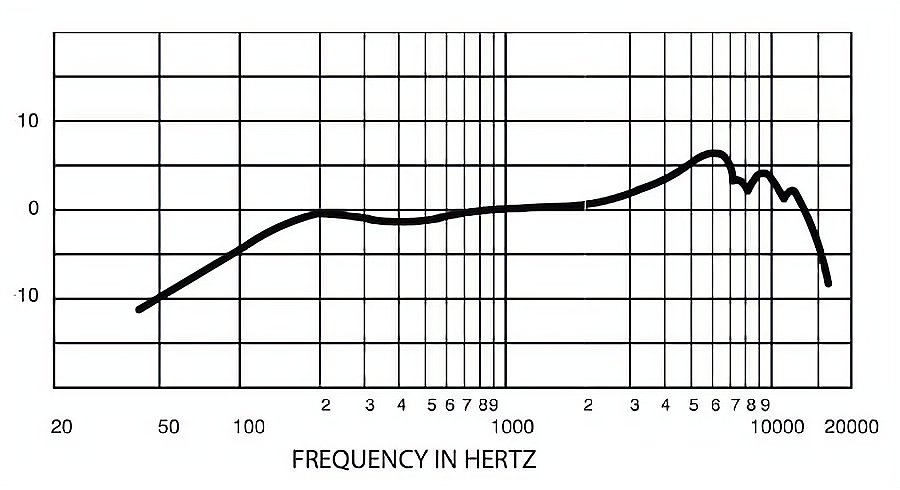
Une caisse claire a généralement des fréquences fondamentales fortes dans la plage de 100 Hz à 250 Hz, avec un pic supplémentaire entre 3 kHz et 6 kHz pour son caractère harmonique supérieur. Les caisses claires sont généralement enregistrées avec des microphones dédiés afin de mettre en valeur leur son unique tout en les isolant des autres éléments de la batterie.
Caractéristiques principales de la réponse en fréquence adaptée aux caisses claires :
- Low-End Roll-Off : Filtre les bruits de basse fréquence provenant d'autres composants de la batterie.
- Accentuation des médiums-aigus : Accentue l'impact rythmique et les qualités tonales de la caisse claire.
- Atténuation des hautes fréquences : Réduit les interférences des cymbales et autres éléments haut de gamme.
4. Réponse en fréquence pour l'enregistrement d'un piano
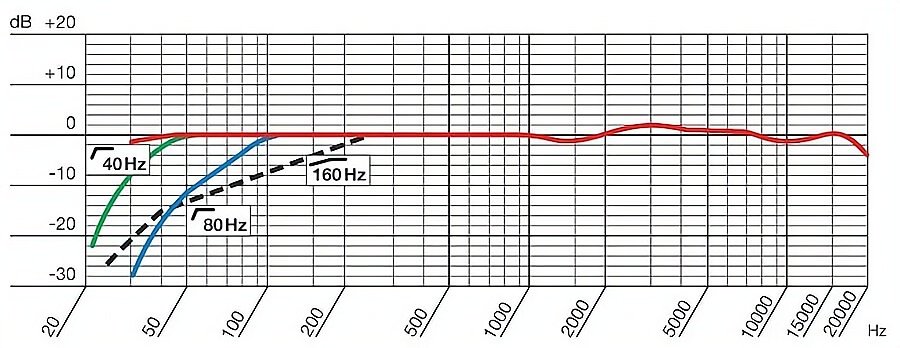
Les pianos ont une large gamme de fréquences et sont mieux captés avec des microphones qui ont une réponse en fréquence plate et étendue. Dans un environnement d'enregistrement, tel qu'une salle de concert, la réverbération naturelle et l'acoustique de l'espace sont cruciales pour obtenir un son de piano authentique. Les microphones omnidirectionnels fournissent souvent les résultats les plus naturels dans ces scénarios.
Caractéristiques principales de la réponse en fréquence pour les pianos :
- Réponse en fréquence plate : Permet de reproduire fidèlement toute la gamme de sons du piano.
- Gamme dynamique étendue : Capture à la fois les nuances douces et les tonalités puissantes de l'instrument.
- Réflexions sonores précises : Reflète l'acoustique de l'espace d'enregistrement pour une sensation de réalisme.
Le choix du bon microphone avec une réponse en fréquence appropriée dépend de la compréhension des caractéristiques de la source sonore, de l'environnement et de la méthode d'enregistrement. Que vous capturiez des voix, des instruments ou des ensembles entiers, l'attention portée à la réponse en fréquence vous aidera à obtenir la meilleure qualité audio possible pour vos besoins spécifiques.


