Speakers and microphones may seem completely different—one produces sound, the other captures it. However, their fundamental principles are nearly identical, just in reverse. This inversion is especially clear when comparing dynamic microphones and speakers.
Speakers and Dynamic Microphones: The Inversion of Principles
The working principle of a speaker can be simplified as “electromagnetic conversion.” A typical speaker consists of three main parts: the diaphragm, the voice coil (usually made of copper wire), and a permanent magnet. When electrical current passes through the voice coil, it generates a magnetic field, which interacts with the permanent magnet’s field, causing the diaphragm to move. This diaphragm movement displaces air, creating sound waves.
Dynamic microphones operate on the same principle, but in reverse. The core components—a diaphragm, voice coil, and permanent magnet—are the same. However, unlike speakers, microphones use sound waves to move the diaphragm, which in turn moves the attached voice coil within the magnetic field. This induces a voltage in the coil, converting sound into an electrical signal.
In simple terms:
- A speaker uses electrical current to move the diaphragm and produce sound.
- A dynamic microphone uses sound to move the diaphragm and generate an electrical signal. In essence, the speaker is the “reverse” of the dynamic microphone.
Structural Similarities
Speakers and dynamic microphones share strikingly similar components, which are key to their functioning:
- Diaphragm: In both devices, the diaphragm plays a crucial role—generating sound in speakers and an electrical signal in microphones. Its design and material are critical to performance.
- Voice Coil: The voice coil converts electrical energy into magnetic energy in speakers, and vice versa in microphones.
- Permanent Magnet: Both devices rely on a permanent magnet to generate a stable magnetic field, ensuring precise energy conversion.
Different Microphone Types and Their Working Principles
Not all microphones operate on the same principles as dynamic microphones. Some rely on entirely different mechanisms:
- Electret Microphones: These use electrostatic properties, where sound causes changes in capacitance, rather than voice coils or magnets.
- Condenser Microphones: These detect changes in capacitance between the diaphragm and a backplate, without relying on electromagnetic forces..
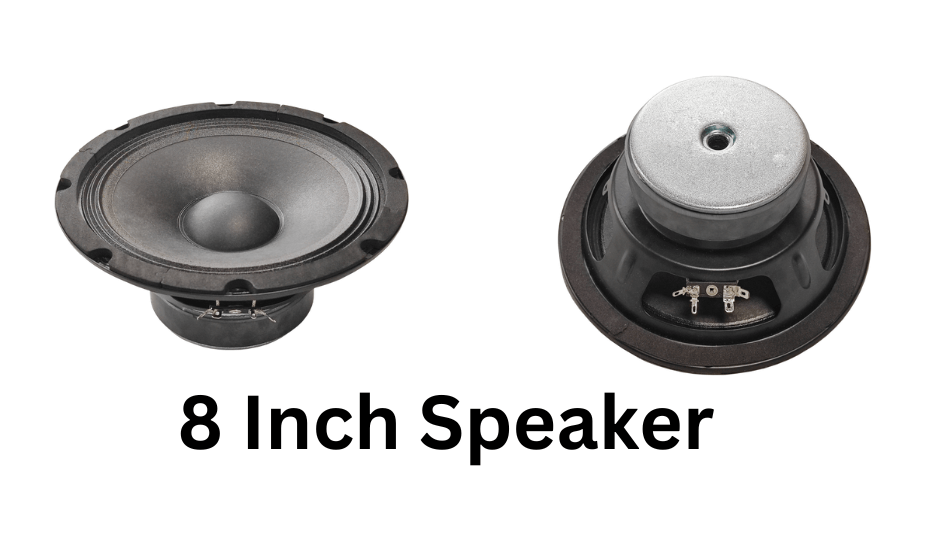
A New Addition to Our Speaker Line: ECM-SP21094-4Ω100W
After exploring the fascinating similarities between speakers and dynamic microphones, we’re excited to introduce our latest model: the ECM-SP21094-4Ω100W speaker. With a 4Ω impedance and 100W power rating, this speaker delivers robust sound, featuring a max SPL of 92dB (1W/1m). Its impressive frequency response of 59Hz to 5kHz makes it ideal for applications ranging from PA systems to high-fidelity audio setups.

Here are the key specifications:
- Model: ECM-SP21094-4Ω100W
- Dimensions: 210 × 94 mm (8 Inch)
- Impedance: 4Ω±15%
- Max SPL: 92dB±3dB Max (1W / 1m)
- Frequency Response: 59Hz~5kHz±3dB 1/3 OCT
If you’re looking for a high-quality, durable speaker that delivers clear and powerful sound, this new unit might be just what you need. Click here to learn more about this product or to place an order.